Gluten-Free Diet – What Is It? Pros and Cons of a Gluten-Free Diet
The gluten-free diet is gaining increasing popularity. But what exactly is it, and who is it meant for? Adopting this type of eating pattern can come with both potential health benefits and certain challenges. Learn about the advantages and disadvantages of a gluten-free diet.
In this article, you will learn:
- Gluten-Free Diet – What Is It?
- Gluten-Free Eating: Then and Now
- Who Is the Gluten-Free Diet For?
- Does a Gluten-Free Diet Lead to Weight Loss?
- Benefits of a Gluten-Free Diet
- Drawbacks of a Gluten-Free Diet
- Impact on Gut Microbiota
- Other Challenges of a Gluten-Free Diet
- Gluten-Free Diet: Pros and Cons – Summary
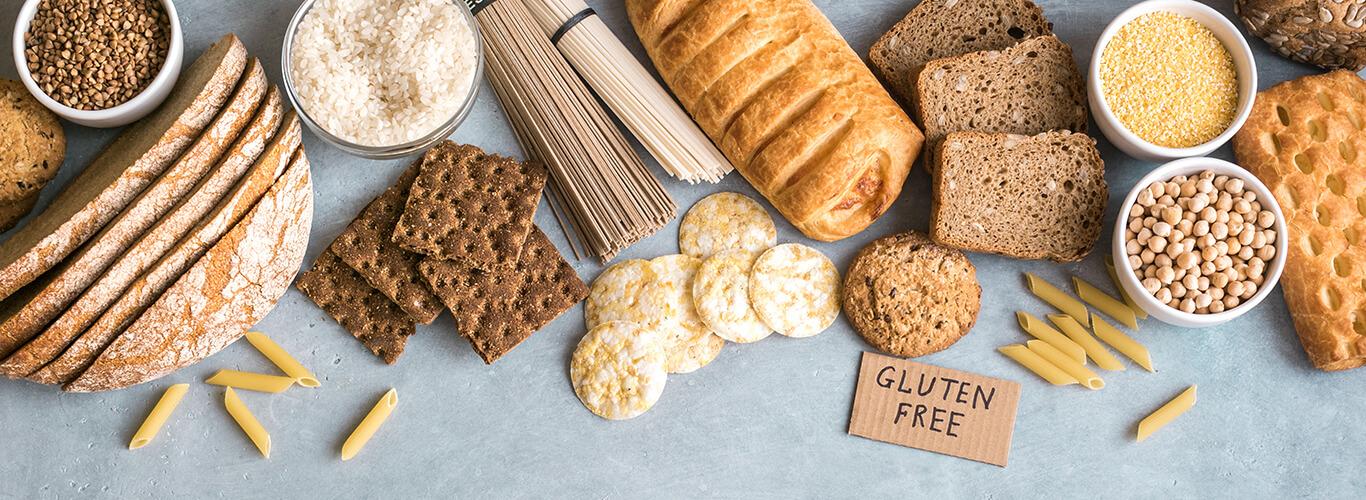

Gluten-Free Diet – What Is It?
A gluten-free diet is an elimination diet that excludes grains containing gluten. The popularity of this dietary approach continues to grow, driven by both trends and a rising prevalence of gluten-related disorders.
Gluten-Free Eating: Then and Now
Initially, a gluten-free diet for people with celiac disease relied heavily on highly processed products that were often bland, less appealing, and expensive. Today, the range of gluten-free products is much wider.
Manufacturers are improving recipes for baked goods to better mimic traditional versions. There’s also an increased focus on naturally gluten-free grains, which are more nutritious.
Who Is the Gluten-Free Diet For?
A gluten-free diet may be particularly beneficial for people whose intestinal villi are damaged by gluten or whose immune system reacts adversely to it. This includes those with:
- celiac disease,
- dermatitis herpetiformis (Duhring’s disease),
- gluten-related allergies or intolerances,
- malabsorption syndromes.
For these conditions, the gluten-free diet is often the only effective treatment, helping alleviate symptoms such as diarrhea, bloating, constipation, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, skin rashes, or weight loss.
Does a Gluten-Free Diet Lead to Weight Loss?
A gluten-free diet is not inherently a weight loss diet and is not suitable for everyone. Eliminating gluten alone does not cause weight loss. To reduce body weight, a caloric deficit is necessary—along with physical activity.
Currently, there is limited credible scientific evidence to support the benefits of a gluten-free diet for people without gluten-related health issues.
Benefits of a Gluten-Free Diet
Potential advantages of going gluten-free include:
- a more varied and diverse menu,
- improved nutritional value of meals,
- lower overall calorie intake,
- increased nutrition awareness among gluten-free dieters.
Expanding the Typical Menu
Eliminating gluten often leads to seeking alternatives, exposing you to new and diverse foods.
Naturally gluten-free grains include:
- quinoa,
- buckwheat,
- amaranth,
- cassava,
- rice,
- teff,
- sorghum,
- millet.
A diet rich in these grains can make your meals more varied and interesting.
Higher Nutritional Value of Naturally Gluten-Free Grains
Naturally gluten-free grains tend to be richer in nutrients than gluten-containing ones. They offer more fiber, B vitamins, and unsaturated fatty acids.
Lower Caloric Intake
Gluten-containing foods are often highly palatable. Reducing their intake may lead to decreased calorie consumption and, indirectly, weight loss.
Wheat-based products such as white bread, pastries, and fast food items (pizza, hot dogs, burgers) are often rich in sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats, but low in fiber.
Removing such items from the diet can reduce the intake of processed, high-calorie foods—though a gluten-free diet is not a guaranteed path to weight loss.
Improved Food Awareness
Adopting a gluten-free diet requires learning and diligence. You begin reading food labels more carefully and become aware of the additives in processed foods.
You also learn to recognize hidden sources of gluten, increasing your overall nutritional awareness.
Drawbacks of a Gluten-Free Diet
Despite the benefits, a gluten-free diet also has disadvantages:
- it can be expensive,
- gluten-free products are often less accessible,
- ready-made gluten-free foods may be nutritionally inferior,
- it may negatively affect gut microbiota,
- it can be socially inconvenient.
Cost of Gluten-Free Products
Gluten-free bread, for example, is typically more expensive than regular bread. The same applies to gluten-free pasta and other items. While manufacturers are making progress, the price point remains high. A cost-saving alternative is preparing meals at home using naturally gluten-free ingredients.
Limited Availability
Although gluten-free product options are increasing, they are not evenly distributed, particularly in smaller towns. Fortunately, more supermarkets and online stores are offering gluten-free products, often marked with the crossed-grain symbol.
Lower Sensory and Nutritional Quality of Gluten-Free Processed Foods
Gluten gives baked goods their elasticity and softness. Without it, bread is often flat, moist, and dense, which negatively affects taste and texture.
Many ready-made gluten-free products are highly processed, low in fiber, and lack key nutrients such as B vitamins, calcium, selenium, zinc, copper, and iron. Relying too heavily on them may lead to nutritional deficiencies.
Low fiber intake can cause constipation, weight gain, and increased risk of gastrointestinal cancers.
Studies also show that gluten-free products often contain higher amounts of sugar and salt, as gluten acts as a flavor carrier.
Many of these items also have longer shelf lives due to added preservatives, colors, emulsifiers, and flavorings.
Additionally, gluten-free products often rely on rice, which may increase exposure to toxic metals like arsenic.
Frequent consumption of corn and its derivatives may also increase the risk of consuming carcinogenic mycotoxins.
Impact on Gut Microbiota
Research suggests that a gluten-free diet may negatively affect gut microbiota, promoting the growth of pathogenic bacteria. This may impair immune function and contribute to digestive issues such as diarrhea, bloating, or constipation.
Other Challenges of a Gluten-Free Diet
One difficulty is the quality of available gluten-free foods. Naturally gluten-free products can sometimes be contaminated with gluten, disqualifying them from being truly gluten-free. Some are even artificially enriched with unnecessary additives.
Social challenges also arise—for example, when traveling or attending events. That’s why education and raising awareness about the need for a gluten-free diet are essential, especially for individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity.
Gluten-Free Diet: Pros and Cons – Summary
So, what is a gluten-free diet and who is it for? Experts primarily recommend it for people with specific medical conditions such as celiac disease or gluten intolerance.
The question “What is a gluten-free diet?” is increasingly searched online, reflecting its growing popularity. If you’re interested in this approach, keep in mind that it’s not for everyone and should not be followed solely for weight loss purposes.
Before starting a gluten-free diet, familiarize yourself with its rules, benefits, and drawbacks. To avoid nutritional imbalances, consult a doctor or dietitian. You can also use the Peater app to help plan a well-balanced gluten-free diet.